Engineered Materials Group
Composite Sealing Systems (CSS) Division
The Ultimate Guide to Bonded Sealing Plates
Applications and Benefits of
Rubber-to-Metal Bonded Gasket Seals
Bonded sealing plates are known by many names and are sometimes described using related terms, such as rubber-to-metal bonded gasket seals, composite sealing plates, elastomeric seals with metal carriers, carrier plate gaskets, overmolded gaskets, and edge-bonded sealing plates. Parker Hannifin's CSS Division uses branded terms for these customized, high-quality products: Gask-O-Seal®, Integral Seal™ and bonded washer gaskets. Such specific terms may encompass a wider range of products, so it is particularly important to use specific technical specifications when ordering or discussing sealing plates to ensure you are referring to the exact component you need.
Despite the many monikers, bonded sealing plates are versatile components that play a crucial role in various industries. When customized to exacting equipment specifications, they not only provide external sealing and separate different media but also transmit forces between mating flanges to ensure reliable sealing.
This blog post will use the generic term “bonded sealing plates” to explore what bonded sealing plates are, their advantages, how they work, and the different types available.
What are Bonded Sealing Plates?
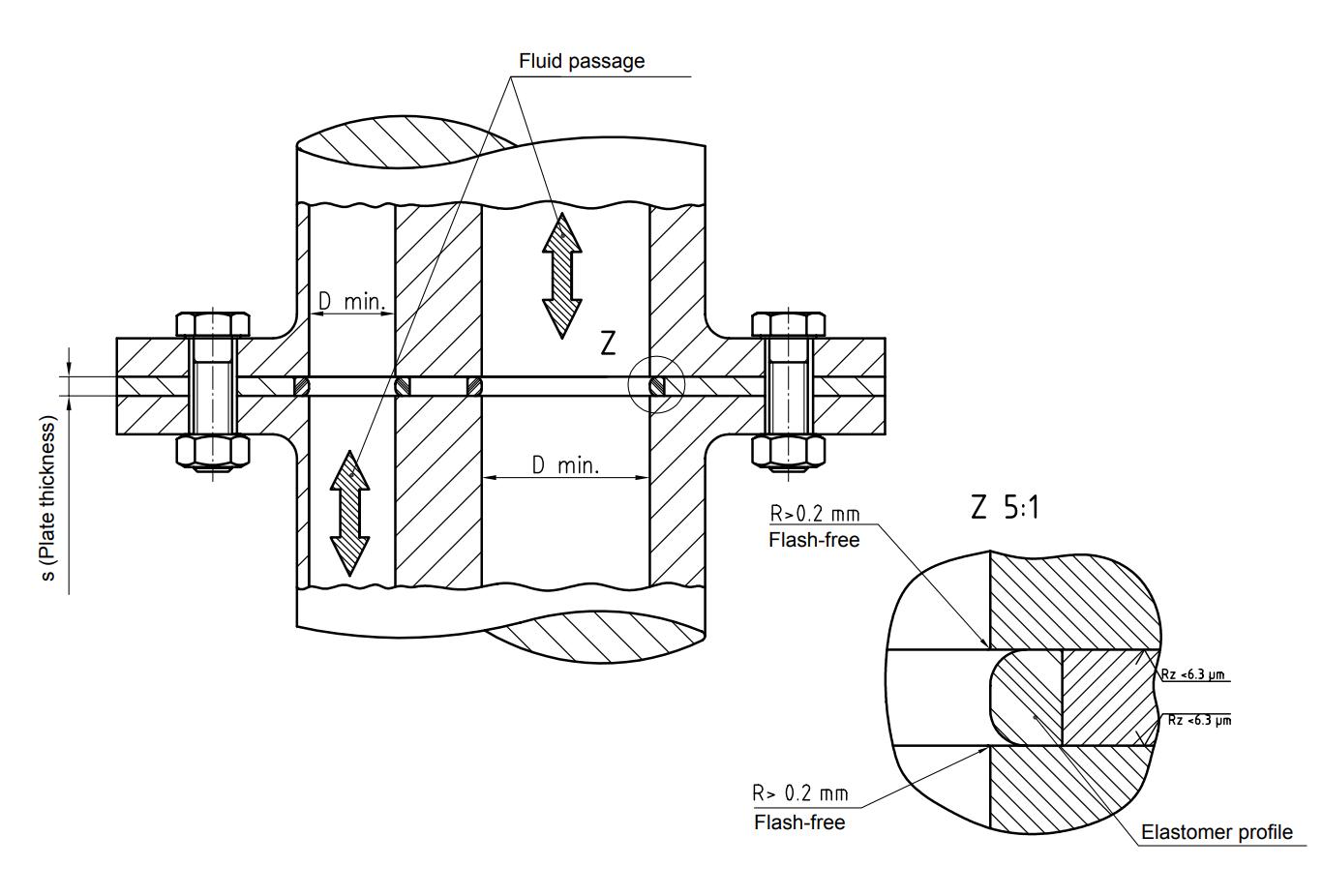
Bonded sealing plates are composite parts consisting of a carrier element with a vulcanized elastomer profile. They are particularly suitable for use as quasi-static sealing elements in flange areas. Depending on the specific requirements, different sealing plates, materials, and configurations are specified. For instance, rubber-coated sheet metal is ideal for sealing gases, while a rubber lip vulcanized to the metal edge is designed for sealing hydraulic oils.
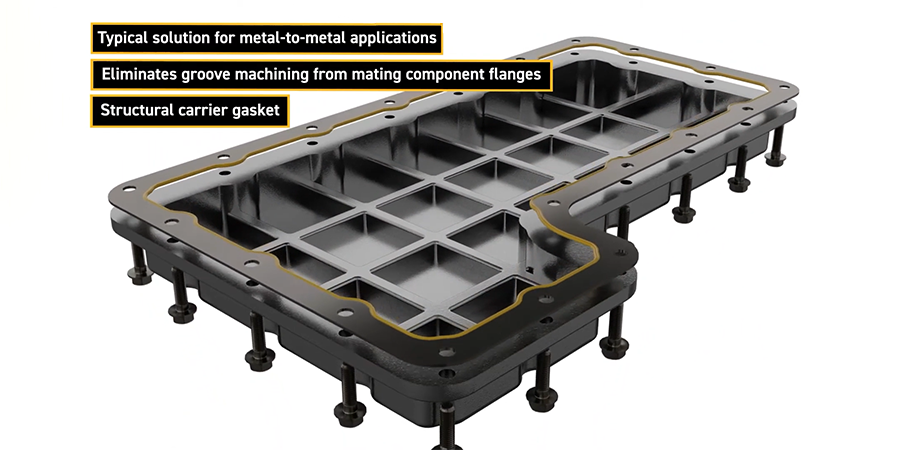
Advantages of Bonded Sealing Plates
Bonded sealing plates offer several convincing advantages, including:
- Protection: After installation, the sealing lip is protected from external influences and internal mechanical overloading.
- No seal groove required: Bonded sealing plates do not require a seal groove in the flanges.
- Reduced component count: Multi-window seals reduce the number of components and potential sources of defects.
- Faster assembly: Automatic installation of bonded sealing plates reduces assembly times.
- Visual inspection: The sealing plate is visible from the outside, allowing for easy visual inspection of the seal installation.
How Do Bonded Sealing Plates Work?
When the flange screw forces compress the vulcanized elastomer profiles of the sealing plate, a force-closed flange connection is created via the seal carrier. The elastomer profile then moves away from the pressure load, and the elastomer's restoring forces provide sealing on a sealing line.
Applications Where Bonded Sealing Plates Are Used
Bonded sealing plates are increasingly used in various industries, such as automotive engineering, aviation, military/defense and space, air conditioning technology, general industrials, oil and gas and life sciences.
They are used exclusively as static flange seals and can be customized for special requirements. Fastener seals, the simplest sealing plate versions, serve as sealing elements at the screw head. They offer advantages in terms of sealing function and can replace metal seals like copper rings. Furthermore, customer-specific sealing plates can be employed for a wide range of media with different elastomers ensuring chemical compatibility.
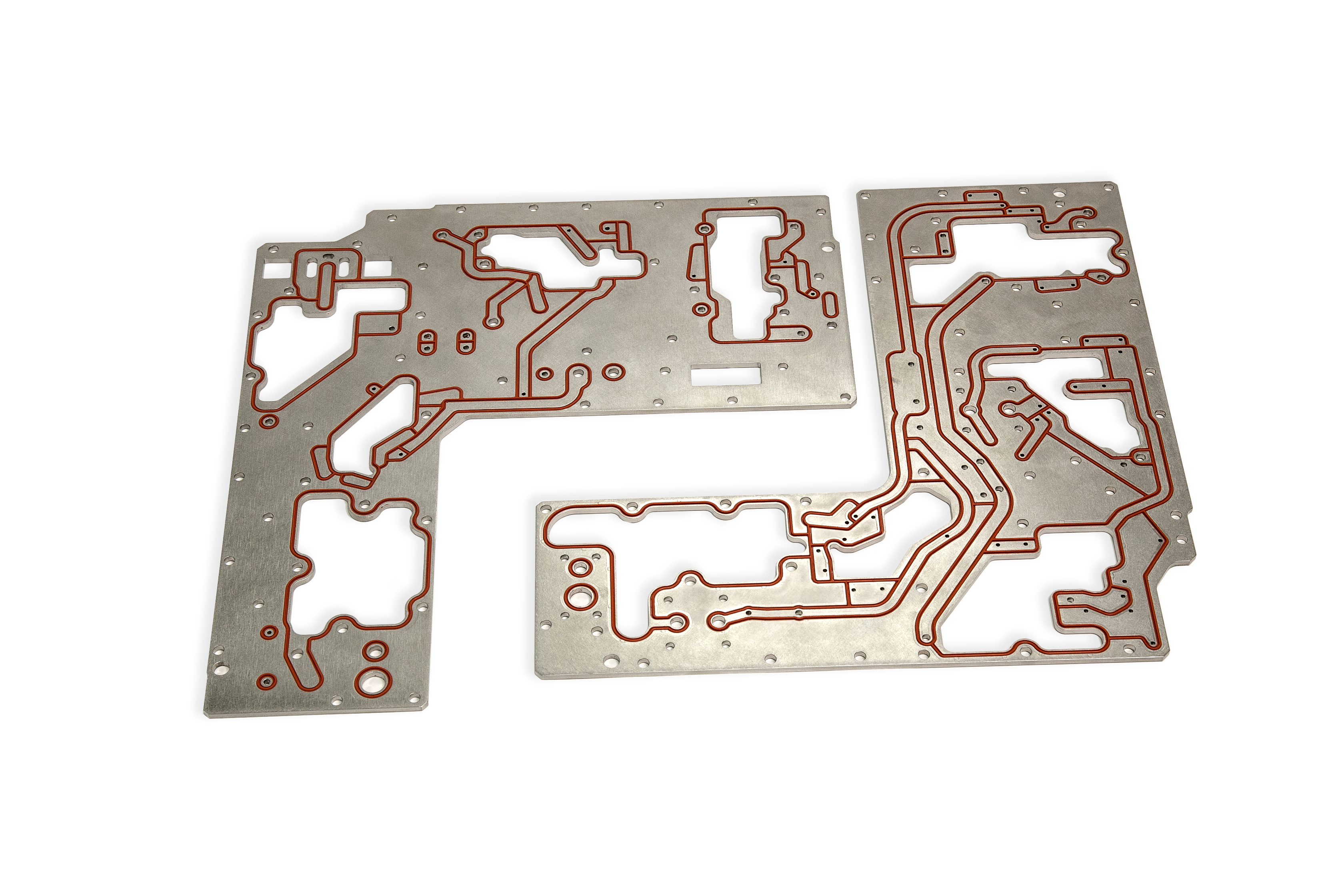
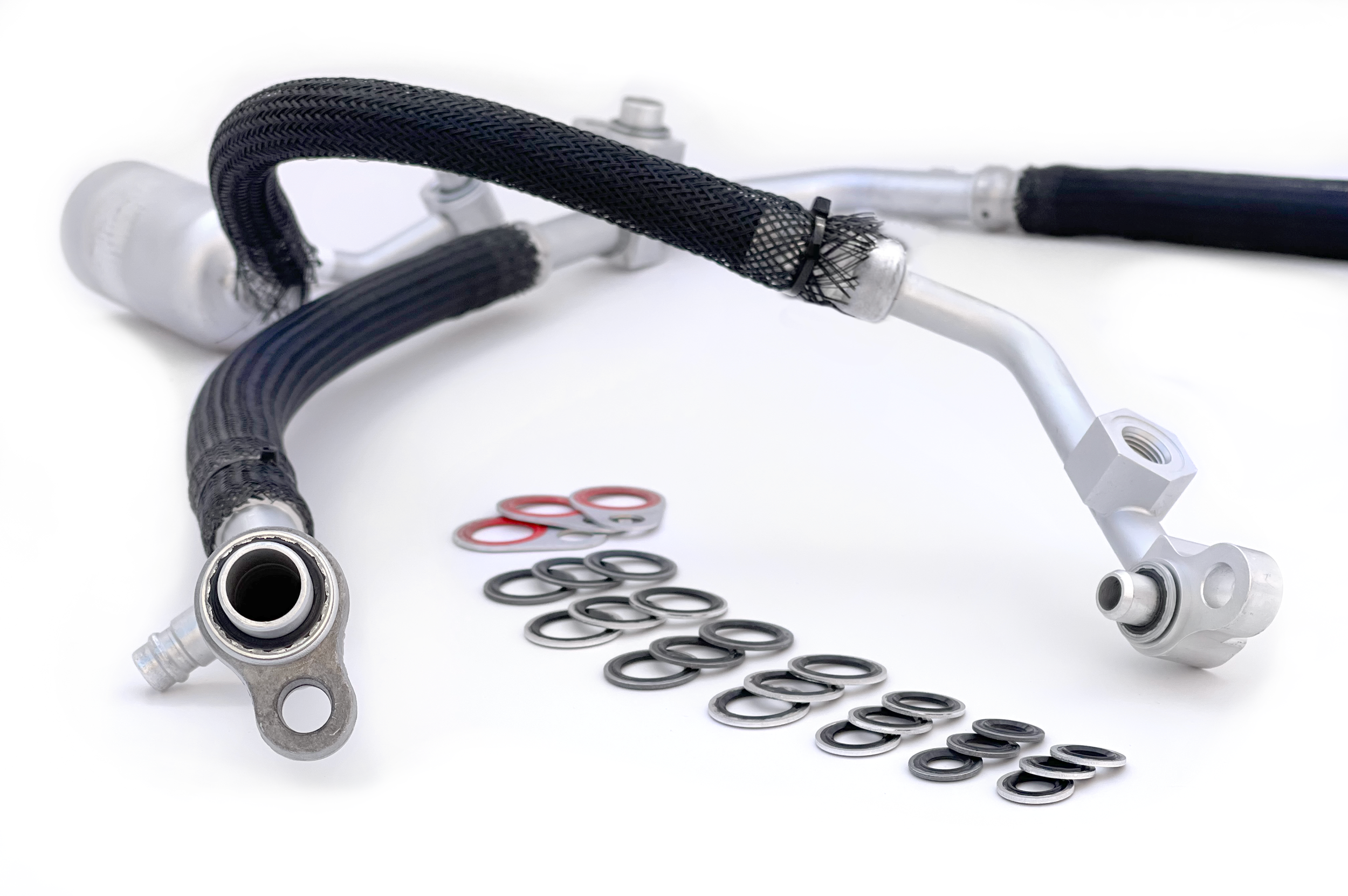
Sealing plates can be engineered to channel fluids like the customized sealing plates shown above.
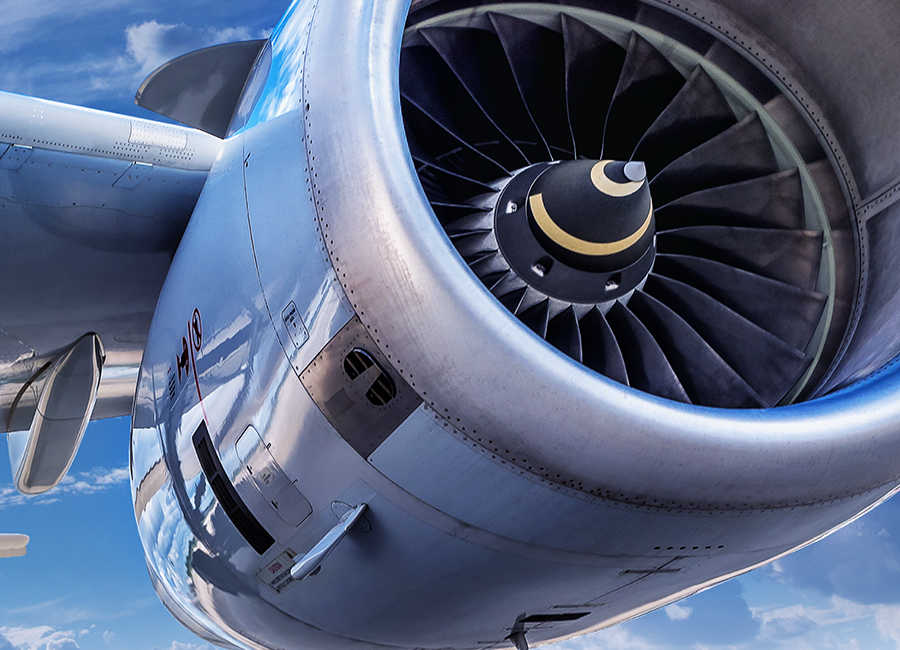

Aviation, Military/Defense and Space
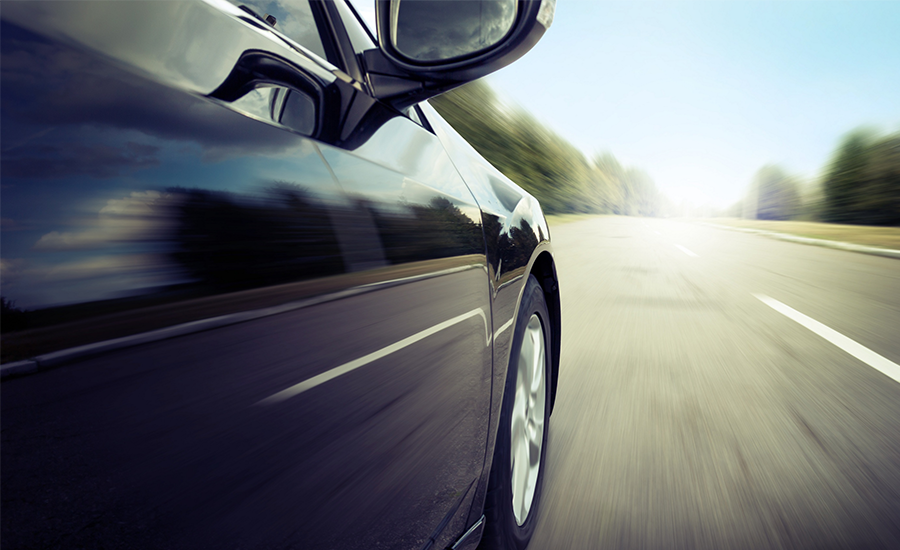

Automotive Engineering (ICE & EV)
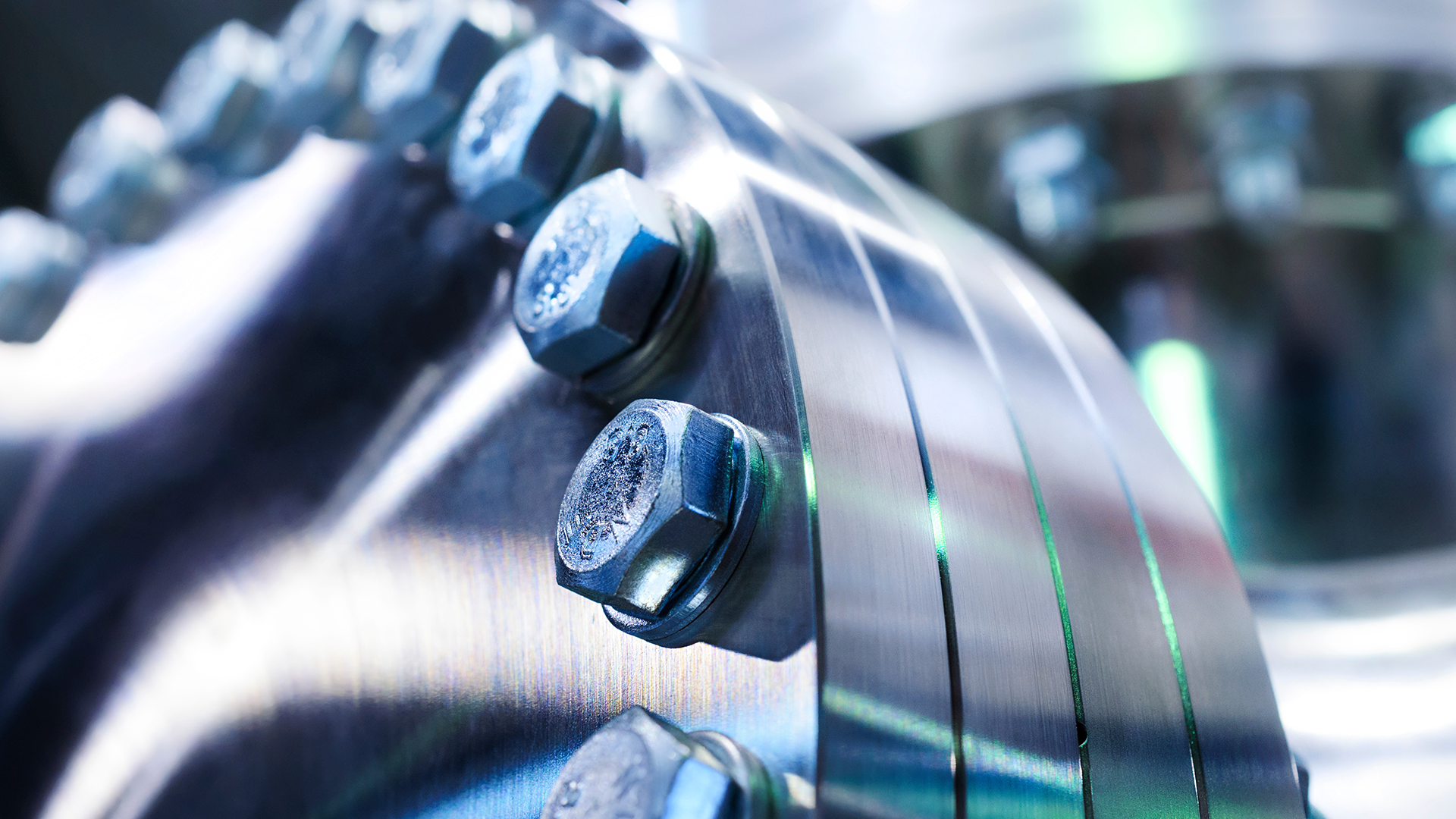

General Industrials

HVAC and Cooling Applications
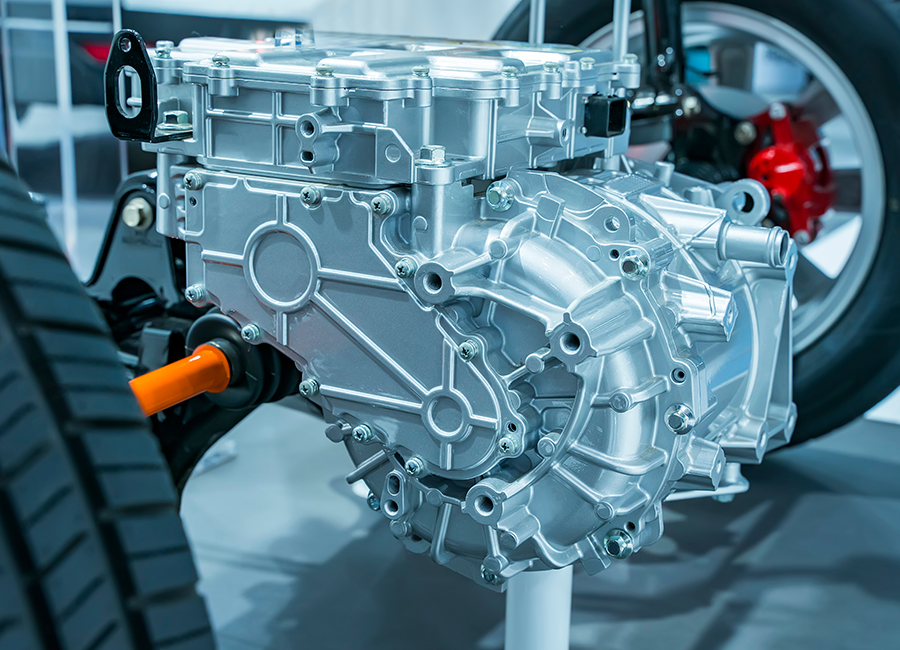
Electric Vehicle Module Applications
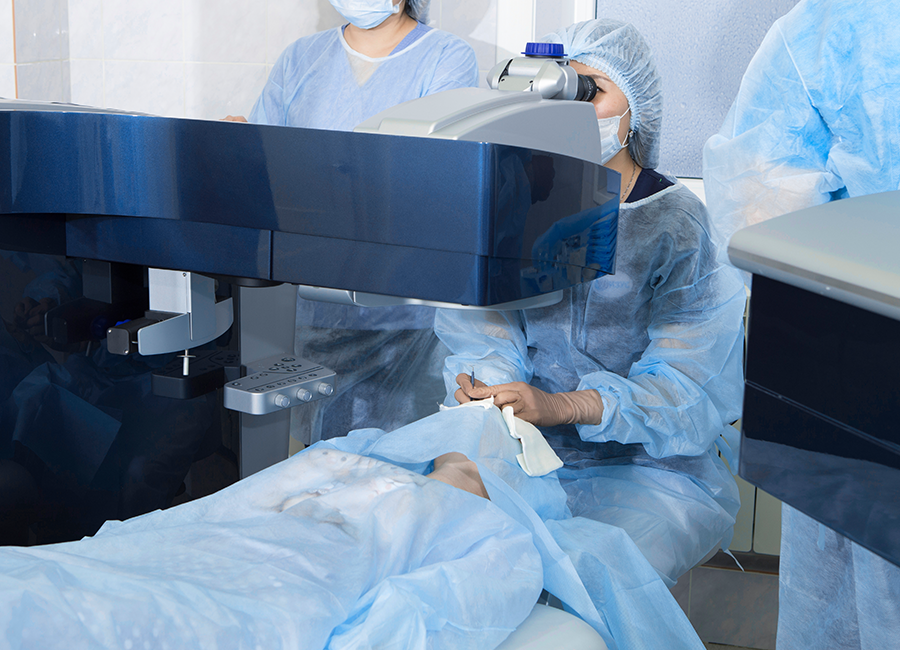
Life Science Medical Equipment
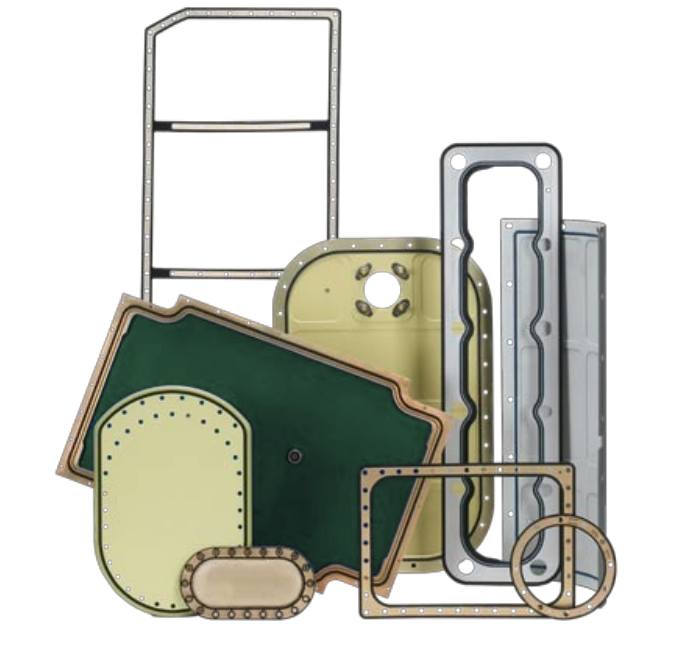
Types of Bonded Sealing Plates
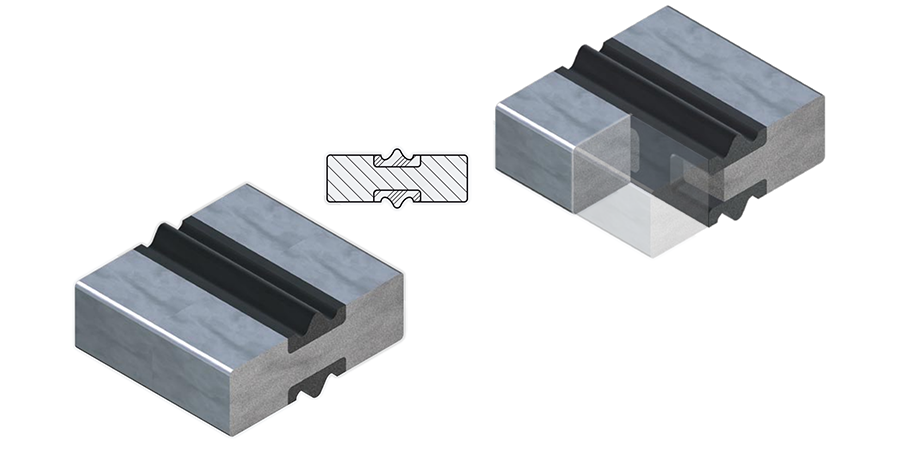
Sealing plates with a molded-in-place elastomer profile. These plates are ideal for long-term installations, offering minimal media contact and protection from mechanical overloading. Bonding techniques may incorporate chemical and/or mechanical bonding mechanisms depending on application requirements.
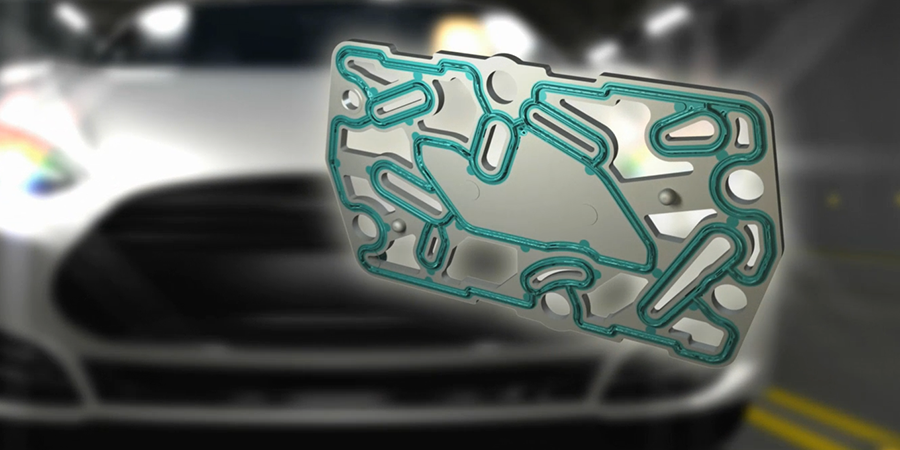
Multiple port overmolded carrier elements: Bonded seals can be highly customized to simplify parts in assembly, provide multiple port or multiple fluid sealing, and reduce tolerance stack-up.
Sealing plates with elastomer profiles vulcanized to the carrier element edge. These are the typical sealing plates for fluid applications, providing face-side flushness with the fluid channel.
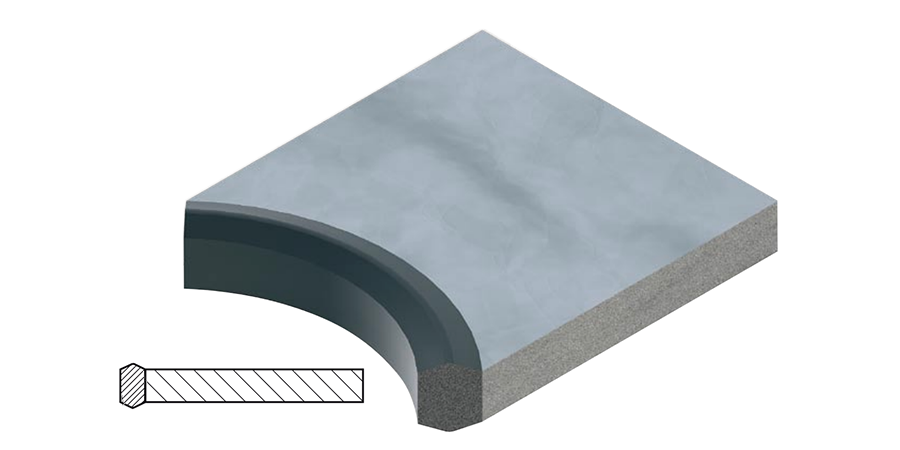
Sealing plates with elastomer profile bonded on lightweight aluminum carrier element: This design allows loading from one side of the flange through the gasket to the mating flange.
Need more information or help with a project?
Are you experiencing challenges with static sealing or require high-quality sealing plates for your application? Parker Hannifin's CSS Division has the qualified materials expertise, state-of-the-art design engineering tools, and comprehensive manufacturing capabilities you need.
Visit www.parker.com/css to explore our capabilities for engineering the perfect solution for your specific requirements. Let us help you optimize performance and reliability today!
TALK TO AN EXPERT
Fill out the form and one of our engineering associates will contact you to discuss solutions for your application.
©2023 Parker Hannifin Corporation | Privacy Policies