Solving EV Charging Station Design Challenges: Thermal Interface Materials and EMI Shielding Solutions
April 11, 2023
Electric vehicle (EV) battery charging stations, also known as EV charging stations or EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), consist of various electronic components and systems that work together to safely and efficiently charge the batteries of electric vehicles. Like most modern, high power electronics, these devices must overcome challenges associate with thermal management and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding in order to operate properly and effectively. In this article we will breakdown the common components of EV charging stations and present solutions to common electrical design challenges.
1. Power Conversion Systems: EV charging stations utilize power conversion systems, such as AC/DC converters or DC/DC converters, to convert the input power (from the grid or a renewable energy source) to the appropriate voltage and current levels required to charge the EV batteries.
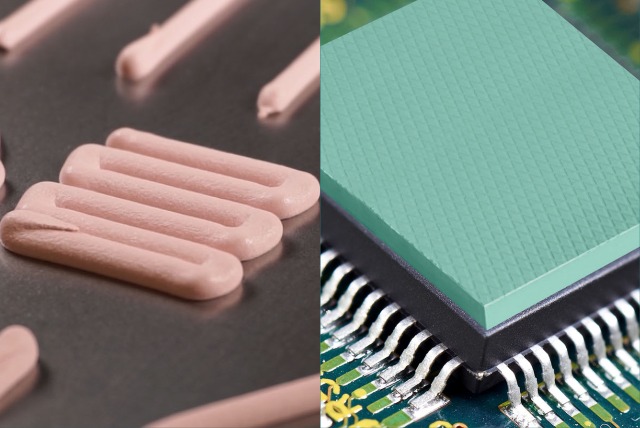
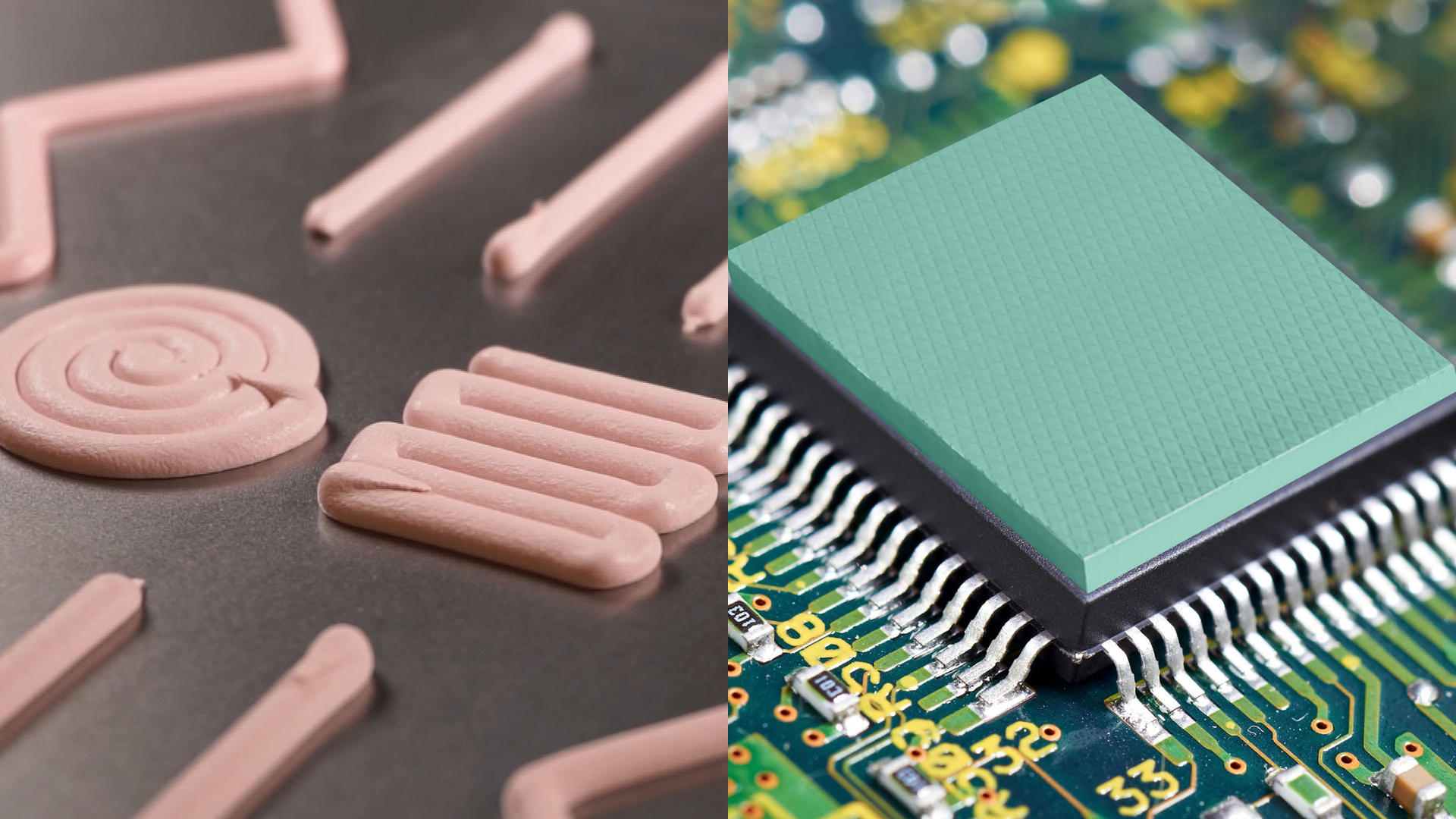
AC/DC converters (also known as rectifiers) generate tremendous amounts of heat and must utilize some sort of cooling feature, often in the form of passive cooling. Thermal Gap Pads or Dielectric/Electrical Insulator Pads provide durability while providing high levels of thermal conductivity to displace air within electronic components
2. Charging Controllers: Charging controllers manage the overall charging process, including communication between the charging station and the vehicle, monitoring the charging progress, and adjusting the charging parameters as needed to ensure safe and efficient charging.
The process of regulating and measuring current or voltage levels in and of itself generates heat that should ideally be dissipated to not disrupt the monitoring process. Thermal gels are great solutions for cooling of specific heat generating components on the printed circuit boards (PCBs) of controllers.
3. Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Most EV charging stations feature some form of HMI, such as displays, touchscreens, or indicator lights, to provide users with information about the charging process, charging status, and any potential issues or errors.
Regardless of the resolution or display outputs, the HMI often serves as a point of EMI weakness unless properly shielded. EMI shielded windows and EMI shielded displays integrated with LCD or touchscreen features are often required to ensure proper electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). These displays can incorporate features such as anti-glare coatings and surface hardening for environmental durability and printed logos or text for commercial or aesthetic benefits.
4. Communication Modules: EV charging stations often incorporate communication modules (such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular connectivity) to enable remote monitoring, control, and diagnostics, as well as to support billing, payment, and other networked services.
Wherever wireless (or wired) communication is present, EMI shielding must be considered. For environmentally protected solutions, conductive foam solutions and board level shielding are economical and simple solutions for meeting EMC compliance. Devices that communicate information such as diagnostics or payment information but be especially careful of harmful interference.
5. Safety and Protection Systems: Various safety and protection systems are integrated into EV charging stations to ensure the safe operation of the equipment and protect both the user and the vehicle. These systems may include ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI), overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and temperature monitoring sensors.
Grounding occurs at nearly every level of electronic device integration within an EV charging station. For sensor and monitoring equipment, fabric-over-foam gasketing is used to provide a reference voltage and mitigate signal noise.
6. Energy Metering: EV charging stations typically include energy metering components that measure and record the energy consumption during the charging process. This data can be used for billing purposes, energy management, and usage analysis.
Like charging controllers and communication modules, these meters must be properly cooled and shielded for proper long-term reliability.
7. Enclosure and EMI Shielding: EV charging stations are housed in enclosures that protect the internal components from environmental factors (e.g., weather, dust, and moisture). Additionally, EMI shielding materials may be used to prevent electromagnetic interference from affecting the performance of the electronics within the charging station.
EV Charging stations come in nearly every shape, size, and color but every single one is tested to rigorous industry standards. Enclosures must not only protect the valuable internal electronics from the environment but also from stray signals coming from telecom equipment, nearby vehicles, cell phones, and other devices. Conductive elastomer gaskets provide the perfect combination of environmental sealing and EMI shielding, able to protect devices from driving wind and rain, and even harsh chemicals. Conductive plastic housings provide design flexibility for individual electronic modules within the device while specialty materials such as conductive coatings and sealants provide an additional layer of shielding at interfaces.
8. Cooling Systems: Some high-power EV charging stations, particularly those that support fast charging, may include active or passive cooling systems to manage the heat generated by the electronic components during the charging process, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the equipment.
Passive cooling systems utilize thermal interface materials to displace air and create the most effective path for heat flow while accommodating mechanical considerations such as manufacturing and assembly tolerances.
Solution Recap:
Thermal Interface Materials
- Thermal Gap Filler Pads
- Durable, low hardness, high conductivity thermal solutions able to be cut to custom sizes for heat transfer in power electronics and electronic modules.
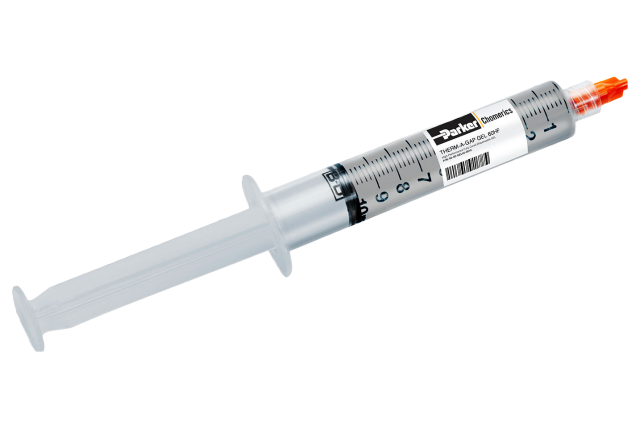
- Thermal Gels (Dispensable Gap Fillers)
- Dispensable, one component, fully cure (no secondary cure required), thermal interface materials that have been tested to rigorous environmental conditions and that can be utilized in small gaps or vertical applications.
- Electrical Insulator Pads (Dielectric Pads)
- Tear-resistant, puncture resistant, thermal interface materials for power electronic cooling and long-term reliability.
EMI Shielding Solutions
- Electrically Conductive Elastomer Gaskets
- Elastomeric gaskets consisting of silicone/fluorosilicone/EPDM binders with conductive fillers meant for high levels of EMI shielding, very low contact resistance grounding, and environmental sealing
- Conductive Foam / Fabric-Over-Foam Gaskets
- Economical EMI shielding and grounding solutions for protected electronics
- EMI Shielded Windows and Displays
- EMI shielded windows and integrated display solutions for protecting screens and information interfaces
- Conductive Plastics
- Conductive injection molded plastics that provide EMI shielding, RF absorption, harsh fluid resistance, and physical impact resistance
- Board Level Shielding
- Highly customizable board level shielding for minimizing cross talk or interference at the PCB level.
- Conductive Coatings and Sealants
- Electrically conductive specialty materials meant to shield non-conductive housings and ensure a continuous conductive path at housing interfaces
These are just a few examples of the types of electronics commonly found in EV battery charging stations. The specific components and systems may vary depending on the charging station's design, power output, and features but all must take into account Thermal Management and EMI Shielding.

Ben Nudelman
Global Market Manager
Parker Chomerics
THERM-A-GAP PAD 80
Parker Chomerics THERM-A-GAP™ PAD 80 Thermally Conductive Gap Filler Pads provide a low hardness (35 Shore 00) solution with 8.3 W/m-K of thermal conductivity. Learn More.
THERM-A-GAP GEL 60HF
THERM-A-GAP GEL 60HF is part of the Parker Chomerics family of fully cured, one component, silicone-based, dispensable thermal interface materials. With a 6.2 W/m-K thermal conductivity, it is designed for high performance heat transfer from electronics components to cooling features and meant to be used across industries and applications. Learn more.
PROVEN PERFORMANCE
Your Partner in Performance.
We continue to advance clean technologies to bring new and enhanced capabilities and efficiencies.
Safeguarding Alternative Energy with Engineering Innovation
Around the world, businesses and consumers alike are turning their attention to alternative energy sources such as solar, wind and biomass conversion. This growing interest isn’t just hype; it’s backed by large investments in green, sustainable energy, and many companies are hard at work developing a broad suite of innovative products to meet the demand.
Thermal Gels or Gap Filler Pads? Top 6 Things You Should Know
Thermal interface materials are used to eliminate air gaps or voids from adjoining rough or un-even mating surfaces. Because the thermal interface material has a greater thermal conductivity than the air it replaces, the resistance across the joint decreases and the component junction temperature will be reduced.
Protect Equipment with a High-Performing Gap Filler Pad
New from Parker Chomerics is the THERM-A-GAP™ PAD 70TP Thermally Conductive Gap Filler Pad. This ultra-soft, ultra-conformable, high-performance product provides a very low hardness (15 Shore 00) solution with 7.0W/m-K thermal conductivity. THERM‐A‐GAP PAD 70TP is designed to provide effective heat transfer between electronic components and their associated cooling features such as heat sinks.
We’re constantly innovating in our drive to create the most advanced clean energy solutions.
2023 Thermal Interface Material Innovations
Over the last year, Parker Chomerics has developed new, state of the art thermal interface materials, or TIMs, for use across industries and applications. These novel products continue to expand the portfolio of high performance, high reliability thermal gap pads and dispensable thermal gels.
Can't find what you're looking for? Talk to one of our experts.